Is An Animals Skin Made Up Of Cells

myCBSEguide App
CBSE, NCERT, JEE Main, NEET-UG, NDA, Exam Papers, Question Banking concern, NCERT Solutions, Exemplars, Revision Notes, Free Videos, MCQ Tests & more.
Install At presentCBSE Biological science Chapter 7 Structural System in Animals class xi Notes Biology in PDF are bachelor for free download in myCBSEguide mobile app. The best app for CBSE students now provides Structural Organisation in Animals class 11 Notes Biological science latest chapter wise notes for quick preparation of CBSE exams and school based annual examinations. Class 11 Biology notes on Chapter 7 Structural System in Animals class eleven Notes Biology are also available for download in CBSE Guide website.
CBSE Guide Structural Organisation in Animals class xi Notes
CBSE guide notes are the comprehensive notes which covers the latest syllabus of CBSE and NCERT. It includes all the topics given in NCERT class 11 Biology text book. Users tin can download CBSE guide quick revision notes from myCBSEguide mobile app and my CBSE guide website.
Structural Organisation in Animals form 11 Notes Biology
Download CBSE course 11th revision notes for Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals class 11 Notes Biology in PDF format for free. Download revision notes for Structural Organization in Animals class 11 Notes Biology and score loftier in exams. These are the Structural Organisation in Animals class 11 Notes Biological science prepared by team of expert teachers. The revision notes help yous revise the whole chapter in minutes. Revising notes in exam days is on of the all-time tips recommended by teachers during exam days.
Download Revision Notes as PDF
CBSE Quick Revision Notes
CBSE Form-11 Biology
Chapter-07
Structural Organisation in Animals class 11 Notes Biological science
In multicellular organism a group of like cells along with intercellular substances perform a specific function. Such organisation is called tissue.
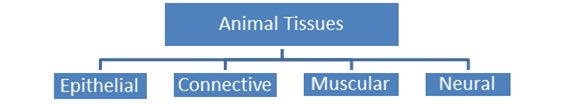
Epithelial Tissue: This tissue provides covering or lining for some part of the body. Cells are compactly packed without intercellular infinite.
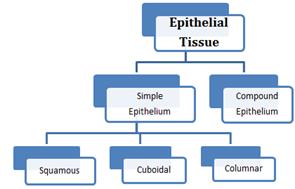
- Simple epithelium is composed of single layer of cells and role every bit lining of torso cavities, ducts and tubes.
- The chemical compound epithelium consists of ii or more ii layers of cells and has protective function.
- The squamous epithelium is made up of single layer of flattened cells with irregular boundaries. They are present in lining of blood vessels, air sacs of lungs.
- Cuboidal epithelium is fabricated up of single layered cube-like cells and found in ducts of glands and tubular office of nephron of kidney for absorption and secretion.
- Columnar epitheliums are made up of tall and slender cells. The nuclei are located at the base. Free surface may have microvilli constitute in lining of breadbasket and intestine. The ciliated ane are called as ciliated epithelium.
- Columnar and cuboidal epithelium specialized for secretion are known as glandular epithelium, which may be unicellular as in goblet cells of gastrointestinal tract or multicellular as in salivary gland.
| Endocrine glands | Exocrine glands |
|
|
- Main function of compound epithelium tissue is to provide protection against chemical and mechanical stress. They encompass the dry out surface of skin, moist surface of buccal cavity, etc.
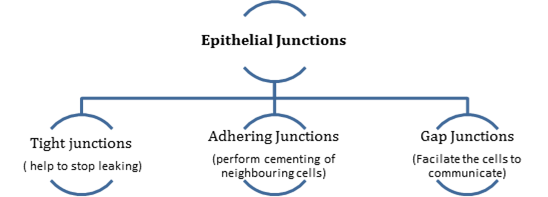
- Epithelial cells are held together by intercellular fabric to form specialized junction.
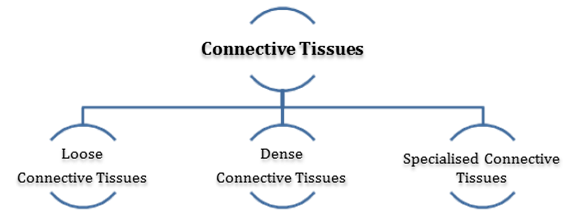
Connective Tissues: They are most abundant and widely distributed tissues which link and support the other tissues. All connective tissues except claret cells, secrete fibres of structural protein called collagen or elastin to provide elasticity and flexibility.
- Loose Connective Tissues contain cells and fibres loosely arranged in semi-fluid ground substance. It includes areolar tissue and adipose tissue.
| Areolar Connective Tissue | Adipose Connective Tissue |
|
|
- Dense connective Tissue contains fibres and fibroblast compactly packed. The orientation of fibres may exist regular or irregular design.
- In dense regular connective tissues collagen fibres are present in rows between parallel bundles of fibres equally in tendons and ligaments.
| Tendon | Ligament |
|
|
- Cartilage, bones and blood are specialized connective tissue.
| Cartilage | Os |
|
|
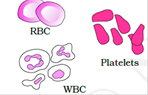
- Claret is fluid connective tissue containing plasma, blood-red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. It helps in transportation of various substances between organs.
Muscle Tissue
- Each muscle is made upwardly of long cylindrical fibres arranged parallel to each other. Fibres are equanimous of fine fibrils called myofibrils. Musculus fibres contract and relax in response to stimulation.
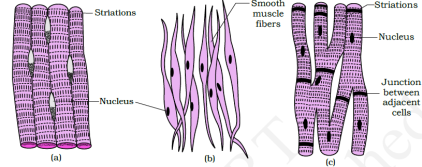
| Skeletal | Smooth | Cardiac |
|
|
|
Neural Tissue
- The unit of measurement of neural system is neuron. Neuroglial cell protects and supports the neuron.
- When neuron get stimulated, electrical impulses are generated that travel forth the plasma membrane (axon).
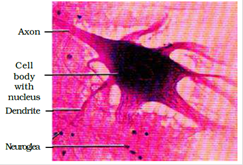
The tissues organize to grade organs which in plow associate to form organ system in multicellular organisms.
Earthworm
- Earthworm is carmine brown terrestrial invertebrate that lives in upper layer of moist soil. The common Indian earthworms are Pheretima and Lumbricus.
- Earthworms have long cylindrical body divided into segments called metameres. The ventral surface contain genital pore and dorsal surface contain mid dorsal line.
- Kickoff trunk segment is called peristomium which contain oral cavity. 14-xvi segments are covered by dark band chosen clitellum.
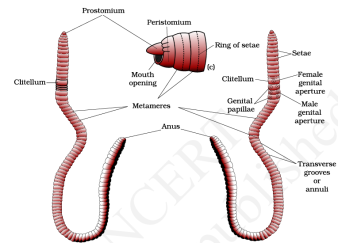
- Single genital pore is present on mid ventral line of 14th segments. A pair of male genital pore is present on 18th segment on ventro-lateral side.
- All the segment except 1st , final and clitellum contain S-shaped setae for locomotion.
- Alimentary canal is straight tube from 1st to last segment having, buccal crenel, muscular pharynx, oesophagus that leads to gizzards, which assistance in grinding the soil particles and decaying leaves. Tummy and small intestine leads to anus.
- Between 26-35 segments, the intestine has an internal median fold called typhlosole. This increases the effective surface area of assimilation in the intestine.
- Airtight vascular system consists of center, blood vessels and capillaries. Blood glands are present on the 4th, 5th and sixth segments. They produce blood
cells and haemoglobin which is dissolved in blood plasma. - Earthworms lack respiratory organs and respire through moist skin.
- Excretory organs is coiled segmental tubules called nephridia. In that location are three types of nephridia: Septal nephridia, integumentary nephridia and pharyngeal nephridia.
- Nervous system is represented by ganglia arranged segmentwise on the ventral
paired nerve cord. The nervus cord in the anterior region (third and 4th segments) bifurcates and joins the cerebral ganglia dorsally to form a nervus ring. - Earthworm is hermaphrodite. 2 pairs of testis is nowadays in tenth and 11th segment. Prostrate and spermatic duct open up to surface as male genital pore on 18th segment.
- 1 pair of ovaries is attached to the intersegmental septum of 12th and 13th segments. Female genital pore open up on ventral side of 14th segment. Mutual commutation of sperms takes place during mating.
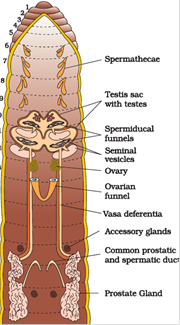
- Mature sperms and egg cells along with nutritive materials are deposited in cocoon in the soil where fecundation takes place.
- Earthworms are known every bit friends of farmer because they make burrows in soil to make it porous for respiration and root penetration. Earth worms are as well used for vermicomposting and as allurement in game fishing.
Cockroach(Periplaneta americana)
- Cockroaches are nocturnal omnivorous organisms that lives in damp places everywhere. The body of cockroach is segmented and divisible into head, thorax and abdomen. The body is covered past hard chitinous exoskeleton.
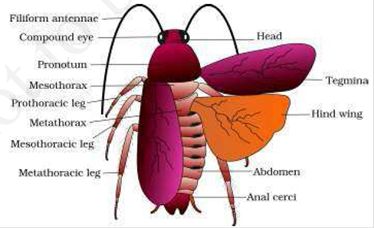
- Head is triangular in shape formed by fusion of half-dozen segments to show flexibility. Head bears compound eyes. Antenna attached on head aid in monitoring the environment.
- Thorax consists of three parts- prothorax, mesothorax and metathorax. Forewings and hind wings are attached with thorax. Belly consists of 10 segments.
| Male Cockroach | Female person Cockroach |
|
|
Digestive Organization of Cockroach-
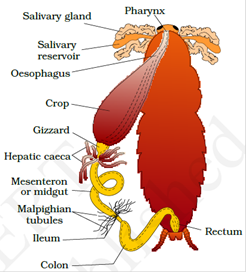
- Alimentary canal is divided into foregut, midgut and hindgut. Food is stored in crop. Gizzard aid in grinding the food particles.
- At the junction of midgut and hindgut yellow coloured filamentous Malpighian tubules are present which assistance in excretion.
- Blood vascular organisation is open up blazon having poorly developed blood vessels. The haemolymph is made of colourless plasma and haemocytes.
- Respiratory system consists of network of trachea which open up through 10 pairs of spiracles on lateral side.
- The nervous organisation of cockroach consists of a series of fused, segmentally arranged ganglia joined past paired longitudinal connectives on the ventral side. Iii ganglia lie in the thorax, and six in the belly. The nervous organisation of cockroach is spread throughout the trunk.
- Each chemical compound middle of cockroach consists of about 2000 hexagonal ommatidia.
With the help of several ommatidia, a cockroach can receive several images of an object. This kind of vision is known equally mosaic vision with more than sensitivity but less resolution, - Cockroaches are dioecious. Male person reproductive system consists of a pair of testes one lying on each lateral side in 4th-6th intestinal segments. The female reproductive organisation consists of two big ovaries situated on 2nd -6th abdominal segments.
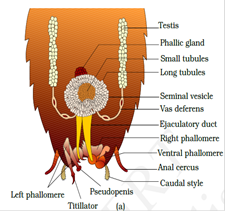
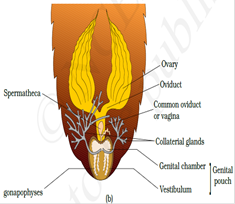
Male reproductive arrangement / Female reproductive organisation
- The fertilized eggs are encased in sheathing called ootheacea. 9 to 10 ootheace are produced by each female.
- Cockroaches are pests and destroys the food, contaminate with evil-smelling excreta.
Frog (Rana tigrina)
Frogs are cold-blooded organism having ability to change colours to hibernate from enemies. Body is divisible into caput and trunk, bulged optics covered by nictitating membrane. Male frog is different from female having vocal sacs and copulatory pad on first digit of forelimb.
- Digestive organization consists of alimentary canal and digestive glands.
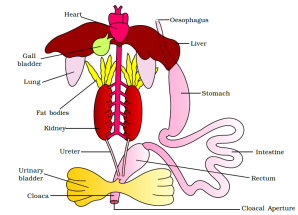
- Digestion starts in tum and terminal digestion occurs in minor intestine. Digested nutrient is absorbed past villi and microvilli present in the inner wall of pocket-sized intestine.
- Skin acts as aquatic respiratory organs (cutaneous respiration). On lands pare, buccal cavity and lungs acts as respiratory organs.
- The vascular organisation of frog is well-developed airtight blazon. Heart is 3-chambered. Blood consist of plasma, RBC, WBC and Platelets.
- Frogs have a lymphatic system consisting of lymph, lymph channels and lymph nodes.
- The elimination of nitrogenous wastes is carried out by a well developed excretory system. The excretory system consists of a pair of kidneys, ureters, cloaca and urinary bladder. The frog excretes urea and thus is a ureotelic animal.
- The system for control and coordination is highly evolved in the frog. It
includes both neural organisation and endocrine glands - Frogs have well organised male and female reproductive systems. Male reproductive organs consist of a pair of yellowish ovoid testes, which are establish adhered to the upper role of kidneys by mesorchium.
The female reproductive organs include a pair of ovaries which are situated
near kidneys. - Fertilisation is external and takes place in water. Development involves a larval stage called tadpole. Polliwog undergoes metamorphosis to grade the adult.
Reproductive systems of frog-
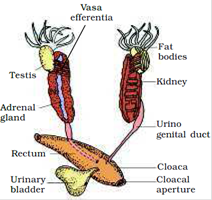
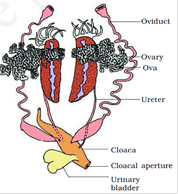
Male person / Female person
Structural Arrangement in Animals class xi Notes
- CBSE Revision notes (PDF Download) Free
- CBSE Revision notes for Class 11 Biology PDF
- CBSE Revision notes Class 11 Biological science – CBSE
- CBSE Revisions notes and Key Points Class eleven Biology
- Summary of the NCERT books all chapters in Biology grade eleven
- Short notes for CBSE class 11th Biology
- Key notes and affiliate summary of Biology course 11
- Quick revision notes for CBSE exams
CBSE Form-11 Revision Notes and Fundamental Points
Structural Organisation in Animals class xi Notes Biology. CBSE quick revision note for class-11 Mathematics, Physics, Chemistry, Biology and other subject are very helpful to revise the whole syllabus during exam days. The revision notes covers all important formulas and concepts given in the affiliate. Even if you wish to have an overview of a chapter, quick revision notes are here to practise if for you. These notes will certainly save your time during stressful exam days.
- Revision Notes for class-xi Physics
- Revision Notes for grade-11 Chemistry
- Revision Notes for class-11 Mathematics
- Revision Notes for course-11 Biological science
- Revision Notes for class-eleven Accountancy
- Revision Notes for class-xi Economic science
- Revision Notes for form-11 Concern Studies
- Revision Notes for class-eleven Computer science
- Revision Notes for class-11 Informatics Practices
- Revision Notes for form-xi Geography
To download Structural Organisation in Animals class eleven Notes, sample paper for course 11 Chemistry, Physics, Biological science, History, Political Science, Economic science, Geography, Computer science, Abode Science, Accountancy, Business Studies and Domicile Science; practice check myCBSEguide app or website. myCBSEguide provides sample papers with solution, exam papers for chapter-wise practice, NCERT solutions, NCERT Exemplar solutions, quick revision notes for ready reference, CBSE judge papers and CBSE important question papers. Sample Paper all are made available throughthe best app for CBSE students and myCBSEguide website.
- The Living Earth class 11 Notes Biology
- Biological Classification class eleven Notes Biology
- Establish Kingdom class xi Notes Biology
- Animate being Kingdom form 11 Notes Biological science
- Morphology of Flowering Plants form xi Notes Biology
- Beefcake of Flowering Plants class eleven Notes Biology
- Structural Organisation in Animals class 11 Notes Biology
- Cell Structure and Functions class 11 Notes Biological science
- Biomolecules class xi Notes Biological science
- Cell Wheel and Cell Division class xi Notes Biological science
- Send in Plants course xi Notes Biology
- Mineral Nutrition class eleven Notes Biological science
- Photosynthesis in college plants class 11 Notes Biological science
- Respiration in Plants class eleven Notes Biology
- Plant Growth and Evolution class xi Notes Biology
- Digestion And Absorption grade 11 Notes Biology
- Animate and Exchange of Gases course 11 Notes Biological science
- Trunk Fluids And Circulation class xi Notes Biological science
- Excretory Products and their Elimination class 11 Notes Biology
- Locomotion and Motion class 11 Notes Biological science
- Neural Control and Coordination class eleven Notes Biology
- Chemic Coordination and Integration class 11 Notes Biology
- Jail cell Structure and Functions grade eleven Notes Biology

Source: https://mycbseguide.com/blog/structural-organisation-in-animals-class-11-notes-biology/
Posted by: collinscapon1936.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Is An Animals Skin Made Up Of Cells"
Post a Comment