Where Is The Vacuole Located In An Animal Cell
Plant Cell Vacuoles
Vacuoles are membrane-bound sacs within the cytoplasm of a cell that function in several different ways. In mature plant cells, vacuoles tend to exist very large and are extremely important in providing structural support, every bit well as serving functions such as storage, waste material disposal, protection, and growth. Many establish cells have a large, single central vacuole that typically takes upwardly most of the room in the cell (80 percent or more). Vacuoles in fauna cells, still, tend to be much smaller, and are more commonly used to temporarily store materials or to transport substances.
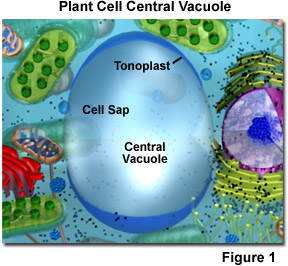
The fundamental vacuole in plant cells (meet Effigy i) is enclosed by a membrane termed the tonoplast, an important and highly integrated component of the plant internal membrane network (endomembrane) system. This large vacuole slowly develops as the jail cell matures by fusion of smaller vacuoles derived from the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. Because the primal vacuole is highly selective in transporting materials through its membrane, the chemical palette of the vacuole solution (termed the cell sap) differs markedly from that of the surrounding cytoplasm. For case, some vacuoles contain pigments that give certain flowers their characteristic colors. The fundamental vacuole too contains establish wastes that taste bitter to insects and animals, while developing seed cells apply the key vacuole equally a repository for protein storage.
Among its roles in plant cell role, the central vacuole stores salts, minerals, nutrients, proteins, pigments, helps in establish growth, and plays an important structural function for the plant. Under optimal weather condition, the vacuoles are filled with water to the point that they exert a significant pressure level against the cell wall. This helps maintain the structural integrity of the plant, along with the support from the cell wall, and enables the institute cell to grow much larger without having to synthesize new cytoplasm. In about cases, the establish cytoplasm is bars to a thin layer positioned betwixt the plasma membrane and the tonoplast, yielding a large ratio of membrane surface to cytoplasm.
The structural importance of the establish vacuole is related to its ability to command turgor pressure. Turgor pressure dictates the rigidity of the cell and is associated with the difference between the osmotic pressure inside and outside of the prison cell. Osmotic pressure is the pressure required to prevent fluid diffusing through a semipermeable membrane separating two solutions containing unlike concentrations of solute molecules. The response of plant cells to h2o is a prime case of the significance of turgor pressure. When a plant receives acceptable amounts of water, the central vacuoles of its cells swell equally the liquid collects within them, creating a loftier level of turgor pressure, which helps maintain the structural integrity of the plant, along with the support from the prison cell wall. In the absenteeism of enough h2o, however, primal vacuoles shrink and turgor force per unit area is reduced, compromising the establish'due south rigidity so that wilting takes identify.
Establish vacuoles are besides of import for their function in molecular degradation and storage. Sometimes these functions are carried out by different vacuoles in the same cell, one serving as a compartment for breaking downwardly materials (similar to the lysosomes found in animal cells), and some other storing nutrients, waste products, or other substances. Several of the materials commonly stored in plant vacuoles take been found to be useful for humans, such as opium, rubber, and garlic flavoring, and are frequently harvested. Vacuoles too often store the pigments that give certain flowers their colors, which aid them in the attraction of bees and other pollinators, but as well can release molecules that are poisonous, odoriferous, or unpalatable to diverse insects and animals, thus discouraging them from consuming the plant.
Dorsum TO Institute CELL STRUCTURE
Questions or comments? Send us an email.
© 1995-2022 by Michael W. Davidson and The Florida State University. All Rights Reserved. No images, graphics, software, scripts, or applets may exist reproduced or used in whatever manner without permission from the copyright holders. Utilise of this website ways you lot agree to all of the Legal Terms and Atmospheric condition prepare forth past the owners.
This website is maintained past our
Graphics & Spider web Programming Squad
in collaboration with Optical Microscopy at the
National Loftier Magnetic Field Laboratory.
Final modification: Fri, November xiii, 2015 at 02:eighteen PM
Access Count Since October 1, 2000: 1335238
Microscopes provided by:
Source: https://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/plants/vacuole.html
Posted by: collinscapon1936.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Where Is The Vacuole Located In An Animal Cell"
Post a Comment